The term "particulate matter" (PM) includes both solid particles and liquid droplets found in air. Many manmade and natural sources emit PM
directly or emit other pollutants that react in the atmosphere to form PM. These solid and liquid particles come in a wide range of sizes.
Particles less than 10 micrometers in diameter (PM10) pose a health concern because they can be inhaled into and accumulate in the
respiratory system Particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter (PM2.5) are referred to as "fine"particles and are believed to
post the largest health risks. Because of their small size, fine particles can lodge deeply into the lungs. Sources of fine particles include
all types of combustion (motor vehicles, power plants, wood burning, etc.) and some industrial processes. Particles with diameters between
2.5 and 10 micrometers are referred to as "coarse." Sources of coarse particles include crushing or grinding operations, and dust from paved
or unpaved roads.
For more information regarding the PM10 and PM2.5 NAAQS, please see the EPA website.
PM10
The nation's air quality standards for particulate matter were first established in 1971 and were not significantly revised until 1987,
when EPA established the PM10 NAAQS, changing the indicator of the standards to regulate respirable particles less than or
equal to 10 microns in diameter (about 1/7th the average width of a human hair).
PM2.5
Ten years later, in 1997, after a lengthy review, EPA revised the PM standards, setting separate standards for fine particles (PM2.5),
equal to or less than 2.5 microns in diameter (about 1/30th the average width of a human hair), based on their link to serious health
problems ranging from increased symptoms, hospital admissions and emergency room visits for people with heart and lung disease, to
premature death in people with heart or lung disease.
In 1997 EPA revised the NAAQS for particulate matter and established primary (health-based) annual and 24-hour standards for PM2.5
[62 FR 38652]. The 1997 annual standard is 15.0 micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3), based on a 3-year average of annual mean PM2.5
concentrations. The 1997 24-hour standard is 65 µg/m3, based on a 3-year average of the 98th percentile of 24-hour concentrations.
[Percentile is a value on a scale that indicates the percent of a distribution that is equal to or below it. For example, a concentration
value at the 98th percentile is equal to or greater than 98 percent of the concentration values.] EPA also revised the secondary
standards, making them equal to the primary standards.
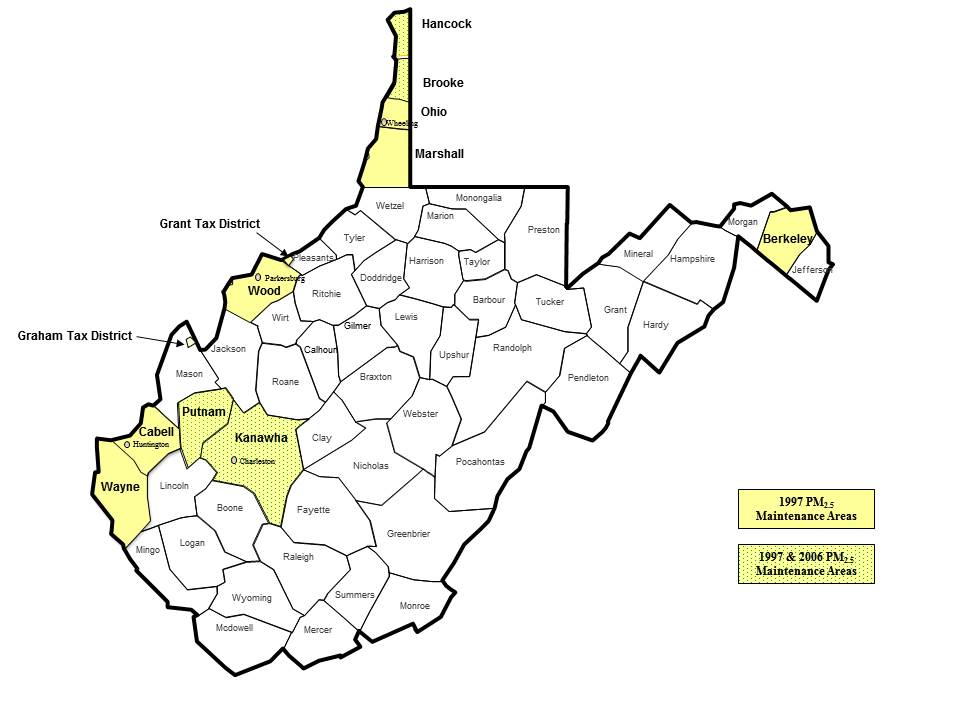
1997 PM2.5 Maintenance Areas
EPA designated 6 areas (ten counties, and 2 partial counties) in West Virginia as nonattainment with respect to the 1997 PM2.5 NAAQS:
- Charleston, WV [Kanawha and Putnam Counties]
- Huntington-Ashland, WV-KY-OH [Cabell and Wayne Counties, and the Graham Tax District in Mason County]
- Martinsburg, WV-Hagerstown, MD [Berkeley County]
- Parkersburg-Marietta, WV-OH [Wood County and the Grant Tax District in Pleasants County]
- Steubenville-Weirton, OH-WV [Brooke and Hancock Counties]
- Wheeling, WV-OH [Marshall and Ohio Counties]
It should be noted that all the areas designated as nonattainment were not in compliance with the annual standard of 15.0 micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3),
based on a 3-year average of annual mean PM2.5 concentrations. However, all areas of West Virginia were found to be attainment with the co-existing 1997
24-hour standard of 65 µg/m3. The design values for the West Virginia nonattainment area monitors for both the annual and 24-hour standards are presented
in this table.
In 2009 EPA determined that the Martinsburg, Parkersburg and Wheeling areas were in attainment with the 1997 standard, based on data for the 3-year
period 2006-2008 [74 FR 60199].
As required by the Clean Air Act, the DAQ submitted demonstrations to EPA for incorporation into the State Implementation Plan (SIP) demonstrating that
the Parkersburg, Charleston, Huntington and Weirton areas would attainment the 1997 standard by April of 2010. As shown in the
table,
data for the 3-year period 2007-2009 shows that these areas did attain the standard.
2006 PM2.5 Maintenance Areas
In 2006, EPA revised the primary 24-hour standard for PM2.5 to 35 µg/m3, based on a 3-year average of the 98th percentile of 24-hour
concentrations. EPA designated 2 areas (4 counties) in West Virginia nonattainment with respect to the 2006 24-hour standard based on
data for the 3-year period 2006-2008 [74 FR 58688].
- Charleston (Kanawha and Putnam Counties)
- Weirton (Brooke and Hancock Counties)
For the subsequent 3-year period, 2007-2009, the Charleston are monitored attainment with the 2006 24-hour standard as shown in the
table.
 PM2.5 Maintenance Areas as of 2015
PM2.5 Maintenance Areas as of 2015